
Blog
Cortisol

Cortisol is one of the most important and key hormones in the human body, closely linked to the concept of stress. This article will examine the role of this hormone and its effects on human health.
Cortisol, known as the “stress hormone,” is naturally produced in the body in response to stressful and tension-filled situations. When a person encounters stress-inducing scenarios, the adrenal glands quickly secrete cortisol. This hormone helps the body cope with challenges and threats. However, the role of cortisol is not limited to responding to stress. It also plays a significant role in regulating metabolism, controlling blood sugar levels, managing blood pressure, and strengthening the immune system. Therefore, maintaining a proper balance of cortisol levels in the body is crucial for overall health.
فهرست عناوین
ToggleWhat is Cortisol and What Role Does It Play in the Body?
Cortisol, known as the “stress hormone,” plays multiple roles in regulating the body’s physiological processes. This hormone is not only secreted in response to environmental stress but also contributes to regulating blood pressure and inflammatory responses. Additionally, cortisol has a significant impact on insulin secretion and can affect blood sugar levels.
The adrenal glands secrete cortisol in response to stimuli from dangerous or stressful situations. This phenomenon, known as the “fight or flight” response, helps humans and other living beings to be prepared and respond effectively to threats. Therefore, the secretion of cortisol is directly related to the concept of survival.
The signal to release cortisol from the adrenal glands is sent by the central nervous system. The amygdala, which plays a key role in processing emotions and anxiety responses, sends messages to the hypothalamus, triggering the release of hormones such as cortisol. In fact, the coordination between the amygdala and the hypothalamus effectively regulates the process of cortisol secretion.
While balanced cortisol secretion is essential for proper body function, excessive secretion of this hormone can lead to serious health issues, such as metabolic disorders and high blood pressure. Therefore, maintaining a balance in cortisol levels is crucial for health.

Symptoms of Excessive Cortisol Secretion
Excessive secretion of cortisol, also known as the “stress hormone,” can have multiple effects on a person’s physical and mental health. Below are some of the symptoms and complications associated with this condition:
- Imbalance in Blood Sugar: Increased cortisol levels can lead to significant fluctuations in blood sugar levels. Individuals experiencing chronic stress may face issues like hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
- Decreased Bone Density: Prolonged cortisol secretion can lead to the breakdown of bone tissue and a decrease in bone density. Over time, this increases the risk of fractures and bone injuries.
- Loss of Muscle Mass: Elevated cortisol levels can cause muscle tissue breakdown, which may result in a decrease in muscle mass. This reduction in muscle mass is often accompanied by an increase in body fat, which is detrimental to health.
- High Blood Pressure: Excess cortisol can cause an increase in blood pressure, raising the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Cognitive Impairments: Excessive cortisol secretion can disrupt cognitive functions, including memory and concentration.
- Increased Abdominal Fat: Accumulation of fat in the abdominal area, especially during middle age, can increase the risk of metabolic and cardiovascular diseases.
- Inflammatory Responses: Excess cortisol can intensify inflammation in the body, which is a contributing factor to many diseases.
- Reduced Immune System Function: High levels of cortisol can weaken the immune system, making the individual more susceptible to infections.
- Slower Wound Healing: Elevated cortisol may slow the healing process of wounds, prolonging recovery time.
- Hypothyroidism: Another consequence of increased cortisol levels is thyroid dysfunction, which can lead to metabolic problems.
- Effects on Cholesterol Levels: Excess cortisol secretion can impact levels of LDL (bad cholesterol) and HDL (good cholesterol), increasing the risk of heart disease.
- Cushing’s Syndrome: Chronic cortisol secretion can lead to Cushing’s syndrome, characterized by symptoms such as elevated blood sugar, excessive thirst, frequent urination, osteoporosis, and depression.
Suggested article: Dopamine
Fluctuations in Cortisol Levels in the Human Body
The level of cortisol hormone in the human body experiences significant changes throughout the day. Typically, cortisol is at its highest level in the early morning and reaches its lowest level during the night. This fluctuating pattern is primarily related to evolutionary reasons and the physiological needs of the body. Therefore, individuals who engage in nighttime activities should be mindful of the hormonal effects on their health.
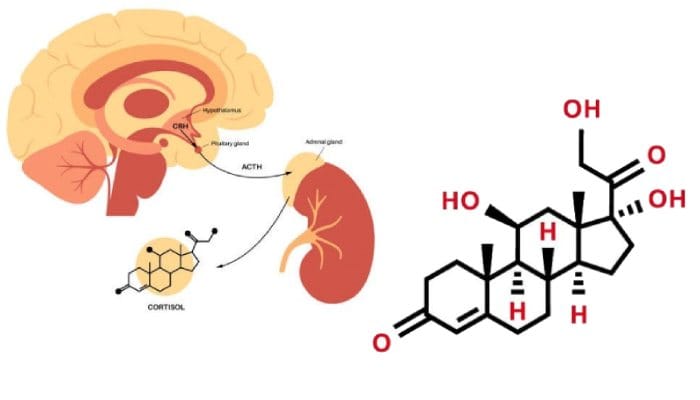
Benefits of Cortisol
It is important to note that cortisol is not only released during the fight-or-flight response, but when stress levels rise, cortisol secretion also increases significantly. For this reason, cortisol is often referred to as the “stress hormone.”
When cortisol is secreted at appropriate levels, it can offer numerous benefits to the body. One of these benefits is the burst of energy it provides during dangerous situations, which aids in survival. In other words, when faced with threats or danger, cortisol secretion helps the individual respond appropriately by increasing energy and alertness.
Additionally, cortisol plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis (internal balance) in the body and can assist in regulating various physiological processes.
Cortisol is the most important glucocorticoid hormone, responsible for regulating the metabolism of fats, proteins, and sugars in the body. It also suppresses inflammation and allergies, and is secreted during stress.
Study article: good and bad stress
6 Methods for Stress Management and Cortisol Reduction
To reduce the secretion of cortisol in the body, stress management is a key and effective approach. Stress is one of the primary factors that increase cortisol levels, and by controlling and managing it, we can help improve the body’s hormonal balance. There are various methods for relaxation and stress reduction that can assist in regulating cortisol levels.
The following methods can be effective in this regard:
- Proper Breathing: Deep and mindful breathing exercises can help reduce tension and stress. This type of breathing increases oxygen delivery to the body and decreases the activity of the sympathetic nervous system.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity not only improves physical health but also has a positive impact on mood and stress reduction. Exercise stimulates the release of endorphins, which create a sense of well-being.
- Guided Imagery: Using imagination to visualize calming and pleasant situations can help reduce stress and create a sense of relaxation in an individual.
- Journaling: Writing down daily thoughts and feelings can help process emotions and reduce mental pressure.
- Listening to Music: Music can have a profound effect on an individual’s mood and is recognized as an effective tool for stress reduction.
- Meditation: For some individuals, meditation and focusing on the mind can assist in reducing stress and increasing inner peace.
- Healthy sex: Positive emotional connection and healthy sex can also help reduce stress levels and improve quality of life.
Finally, it’s important to note that cortisol secretion is influenced by genetic and environmental factors as well. Therefore, stress management techniques and treatment methods may vary for each individual.
برای مشاوره رایگان و رزرو وقت (یا اگر تماس گرفتید و قادر به پاسخگویی نبودیم) شماره تماس خود را وارد کنید. ما به زودی با شما تماس می گیریم!



