
Blog
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)

Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a goal-oriented and structured psychotherapy system based on the principle of reality and problem-solving. This approach is goal-oriented because therapy sessions can be designed according to the type of psychological disorder, making the problem manageable. The focus of cognitive-behavioral therapy is on the thoughts and behaviors that exist in the present moment, and the patient consciously reviews their thoughts. This therapeutic model enables the individual to become their own therapist and, by using the provided techniques, manage challenges independently.
فهرست عناوین
ToggleThe effectiveness of the therapy depends on the collaboration and participation of both therapist and patient, as well as the patient’s consistent use of the techniques. Moreover, this therapy helps prevent relapse of the disorder in the long term.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy works on both cognition and behavior. Inefficient emotions and maladaptive behaviors that lead to psychological disorders are identified and replaced with healthy and rational feelings, thoughts, beliefs, and behaviors through systematic techniques and methods, allowing the individual to experience well-being.
Behaviorism (Behavior Therapy)
Behaviorists considered behavior as the key factor for studying humans and paid little attention to mental processes, thoughts, and reasoning. They believed that behavior is either conditioned or learned through observation. Therefore, learning through observation and conditioning are two main principles in this approach. They hold that every response has a stimulus, and by changing the stimulus, the response can be modified.
The studies of John Broadus Watson (the founder of behaviorism), Burrhus Frederic Skinner, and Joseph Wolpe played important roles in developing this approach. Watson believed that psychology should abandon mental processes, consciousness, content, imagery, and introspective concepts because they are unobservable and unmeasurable, thus falling outside the scientific domain. According to Watson, psychology should be able to predict and control behavior, focusing on observable stimuli and responses and how habits form. This way, psychology becomes a science like other natural sciences.
Cognitive Approach (Cognitive Therapy)
Cognitive therapy is a psychotherapy system developed by Aaron Beck and his colleagues to help individuals overcome emotional problems. This system emphasizes changing people’s thinking patterns to improve their mood, such as depression, anxiety, and anger. Emotional disorders are influenced by cognitive distortions that people create when facing life experiences. These distortions appear as negative interpretations and predictions about everyday events.
In cognitive therapy, effective, positive, and rational cognitive beliefs replace incorrect and negative beliefs.
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT) was developed by clinical psychologist Albert Ellis in the 1950s.
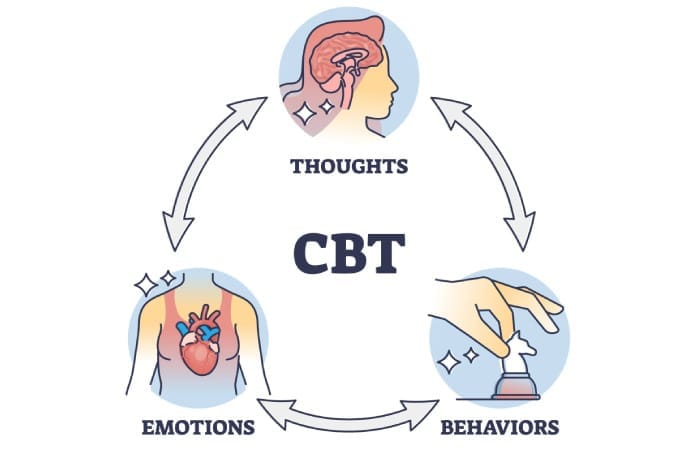
The main premise of REBT is that the way individuals interpret and experience events determines the formation of psychological problems. REBT is based on the idea that there is a causal relationship between thoughts, emotions, and behaviors, and they influence one another.
In other words, in REBT, a person’s thoughts, emotions, and behaviors are considered as a whole, because according to the basic assumption of REBT, how an individual evaluates or perceives an event depends on their mental state and may determine their emotional state. In summary, what affects a person in a given situation is their perception of that situation and the related components of thoughts, emotions, and behaviors, rather than the actual situation itself. These components can affect the person individually or collectively.
Aaron Temkin Beck and Albert Ellis are the founders of cognitive therapy.
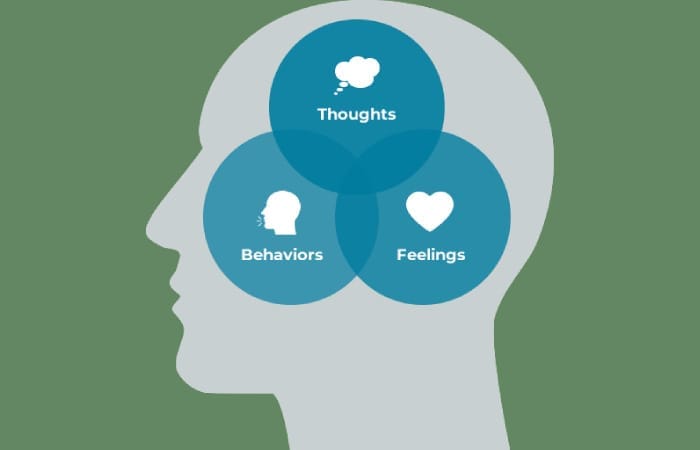
What is the Cognitive-Behavioral Approach?
The cognitive-behavioral approach states that when a person encounters a specific situation, it initially triggers a series of beliefs. These beliefs shape the person’s thoughts. After these beliefs emerge, specific emotions arise within the individual. The belief and thought that appear after facing a particular situation already existed in the person’s mind beforehand.
For example, when a person faces a situation like giving a speech, a particular belief—such as the belief that others will judge them as inadequate—arises in their mind, which leads to feeling anxious.
After the emotion occurs, the next stage is behavior. A person who experiences anxiety tries to avoid attending the meeting or giving the speech. In fact, avoidance of attending the meeting is a behavior that results from the previous stages.
Therefore, being in a situation (A) creates a belief (B) in the person, belief (B) causes an emotion (C), and emotion (C) leads to behavior (D).
For Which Disorders is CBT Effective?
CBT can be effective in treating the following disorders: depression, anxiety, stress, fears and phobias, addiction, relationship problems, eating disorders such as binge eating, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), bipolar disorder. CBT can also help with issues like poor anger control, low self-esteem, and even physical problems such as chronic fatigue and pain.
A skilled CBT therapist teaches their client to perceive surrounding phenomena in ways that cause the least harm. When issues are approached from the right perspective, better use of life’s opportunities is achieved.
برای مشاوره رایگان و رزرو وقت (یا اگر تماس گرفتید و قادر به پاسخگویی نبودیم) شماره تماس خود را وارد کنید. ما به زودی با شما تماس می گیریم!



